Genomics of West Nile Virus
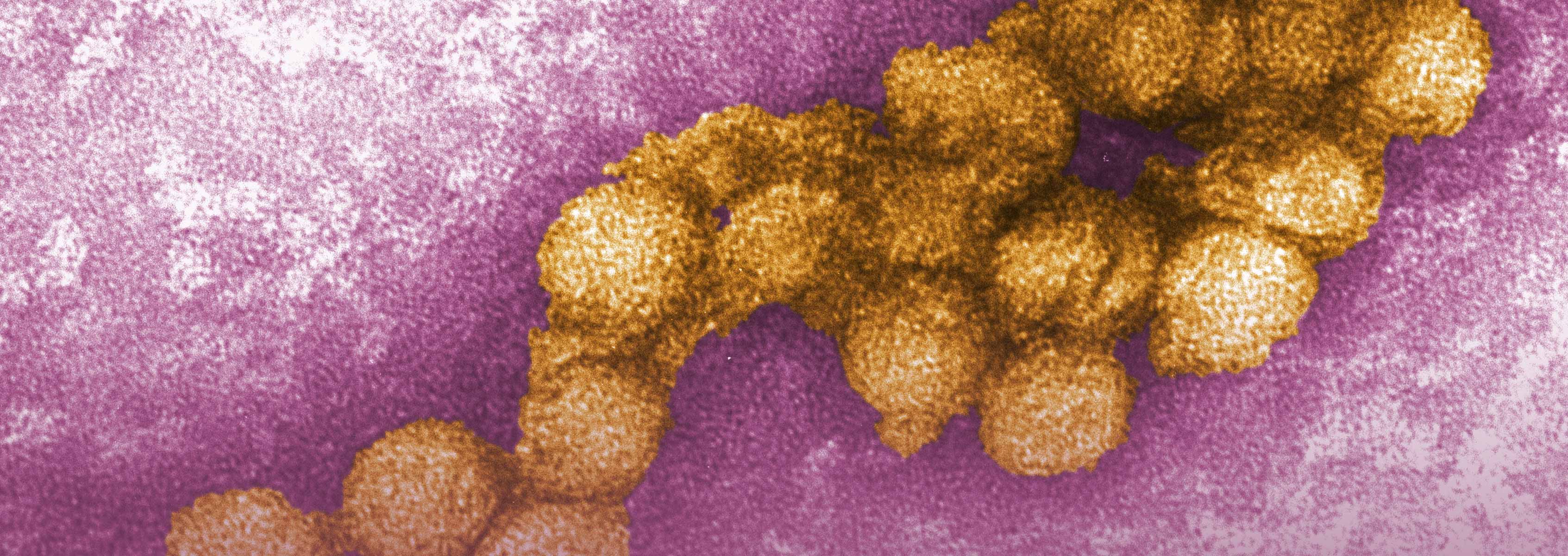
West Nile virus (WNV) is an arthropod-borne virus (arbovirus) that was originally identified in Uganda during the mid-1900’s. Since then, the virus has been found in other African, European, and Asian countries. In addition, WNV emerged as the causative agent in the 1999 outbreak in the United States and has since become endemic in the country. The virus primarily infects birds, horses, and other animals can cause encephalitis or other neurological symptoms in humans.
The goal of this study is to sequence a large collection of strains provided by collaborators to better understand how the sequence diversity of the viruses changes over time within a relatively well-defined geographical area. In addition, generating sequence data with sufficient coverage will allow us to better understand the minor variants that exist as quasispecies within a population. The production, analysis, and interpretation of these data will provide an improved understanding of virus variation and enable the identification of viral protein(s) that could contribute to an effective vaccine.
Funding
This project has been funded in whole or part with federal funds from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services under Award Number U19AI110819.